Wildland Fire in High Latitudes
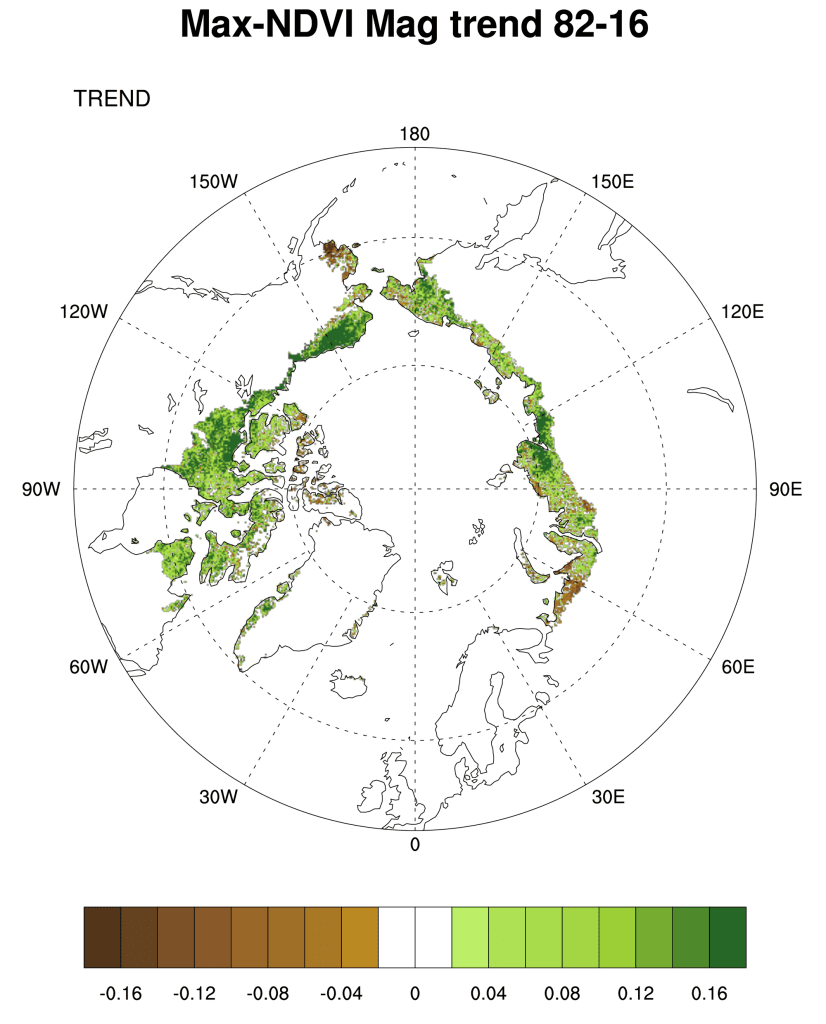
Despite the low annual temperatures and short growing seasons characteristic of northern ecosystems, wildland fire affects both Boreal forest and adjacent tundra regions. In fact, fire is the dominant ecological disturbance in boreal forest, the world’s largest terrestrial biome.
Wildland Fire in High Latitudes Read More »