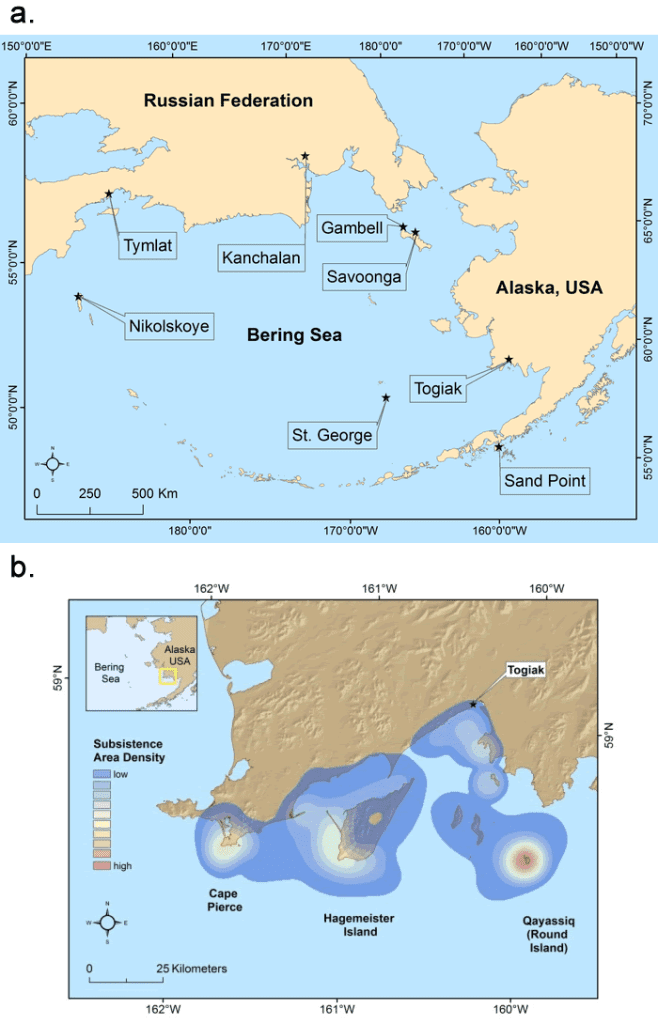
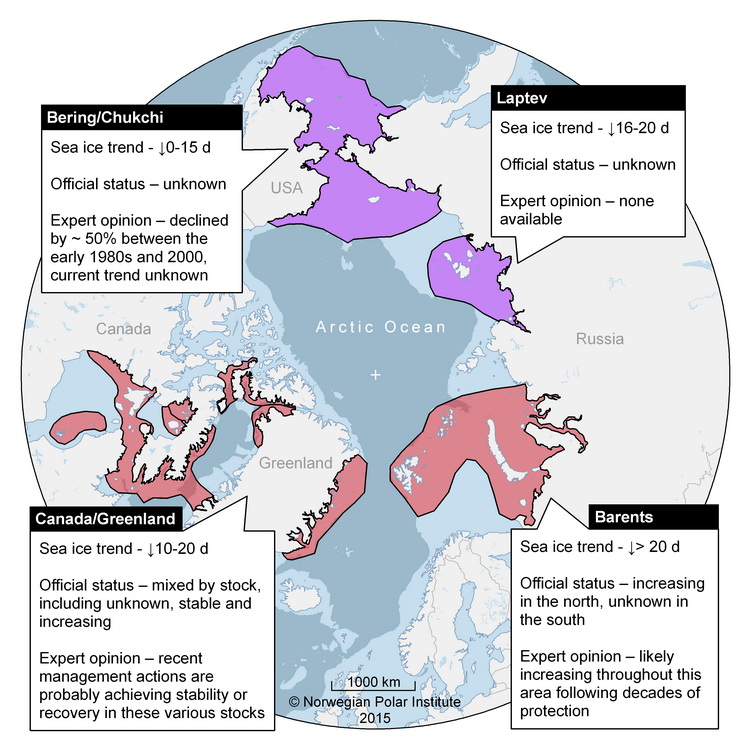
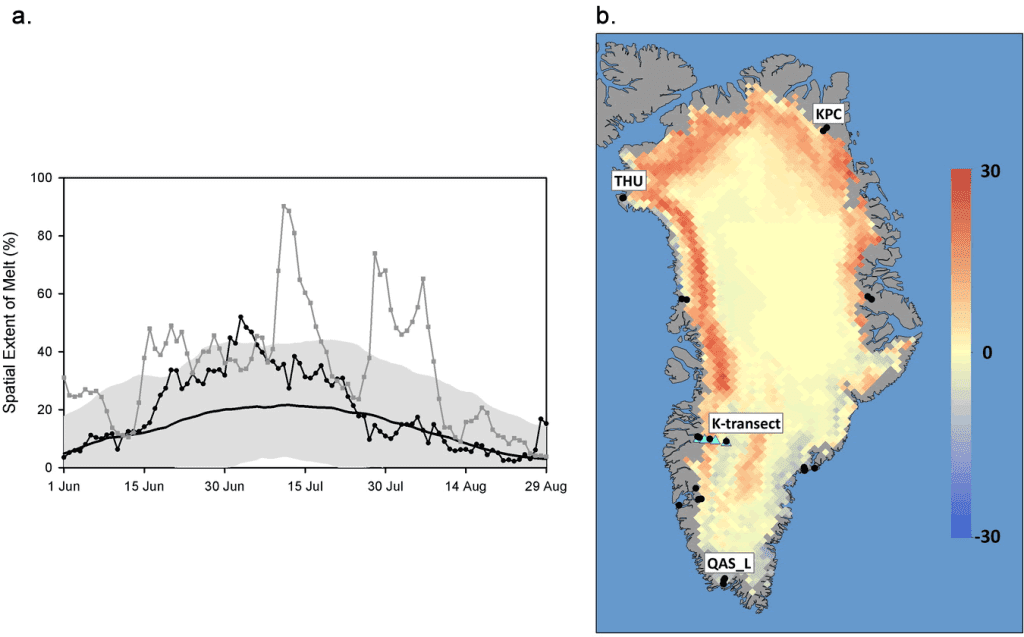
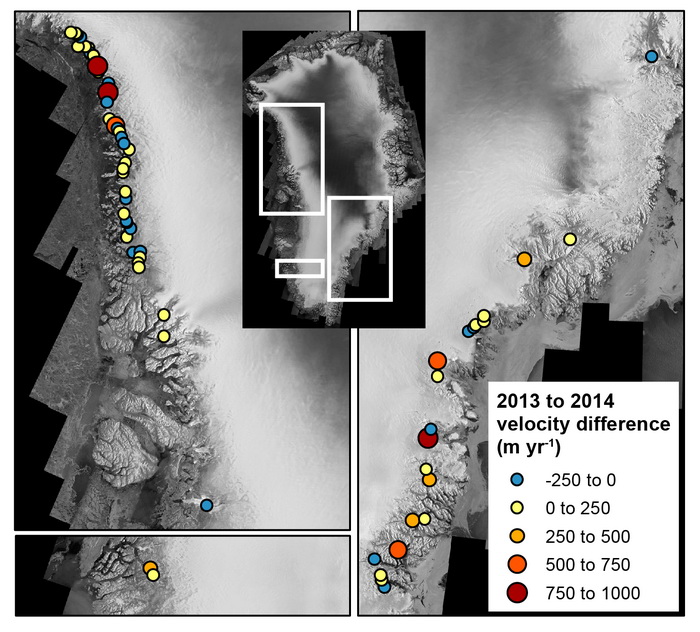
Community-based Observing Network Systems for Arctic Change Detection and Response
Community-based monitoring (CBM) is a broad set of approaches that engage the capacity of community residents in observing and monitoring of a region, e.g., the Arctic (Arctic Council 2015; Johnson et al. 2015). CBM encompasses a continuum of approaches from community-based observing network systems (CBONS), citizen science and observer blogs (Table 11.1).
Community-based Observing Network Systems for Arctic Change Detection and Response Read More »