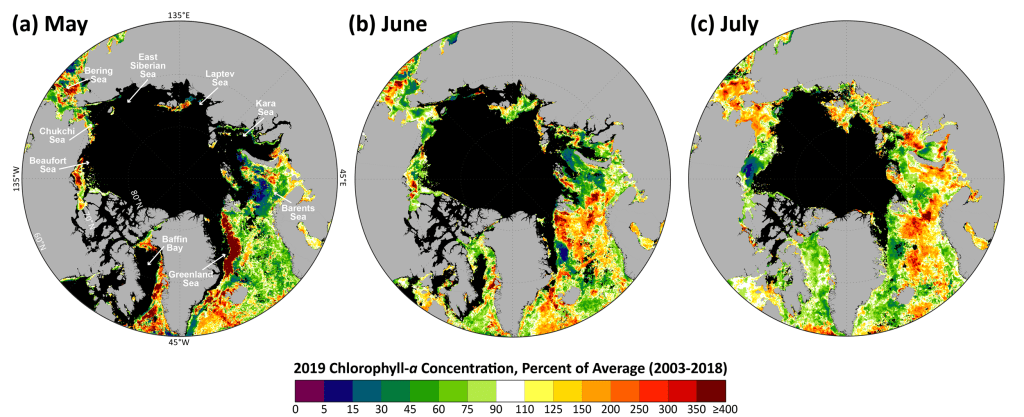
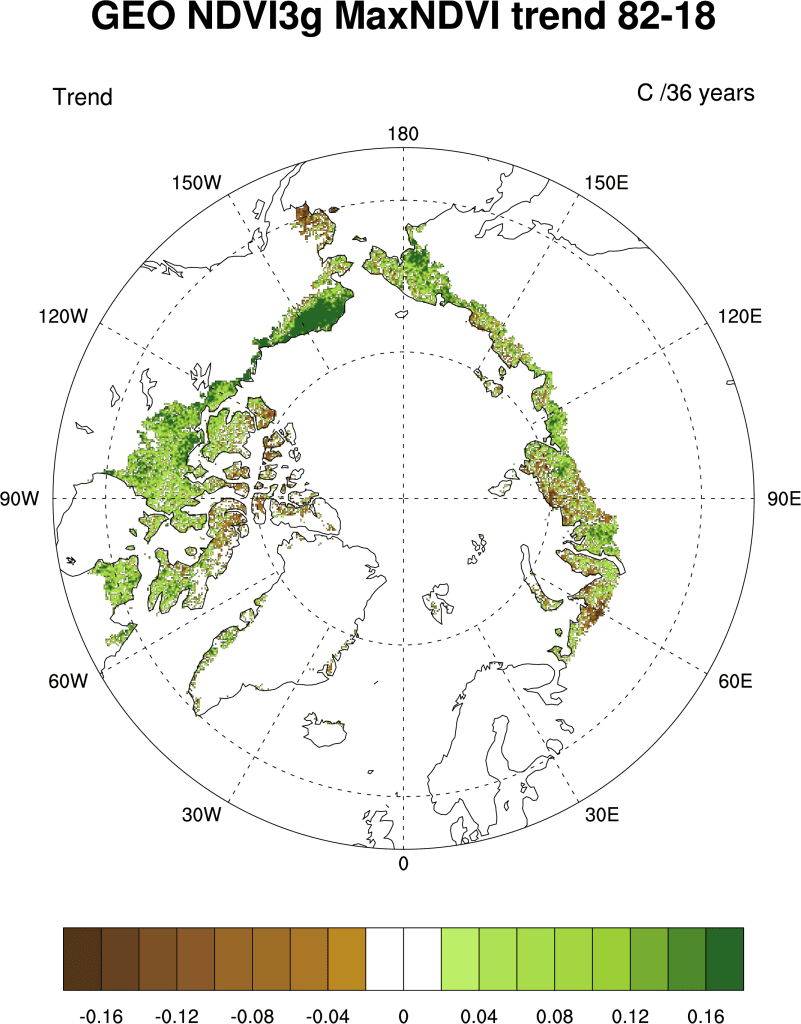
Terrestrial Snow Cover
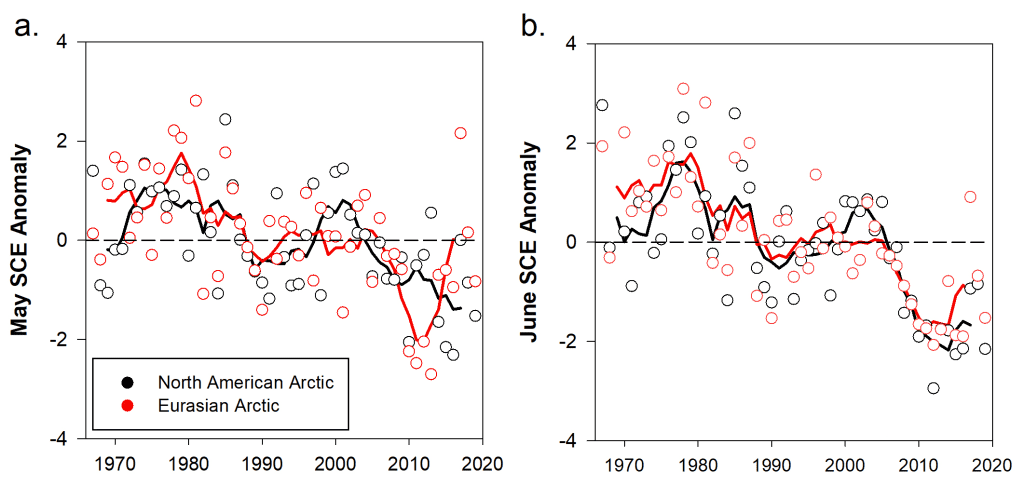
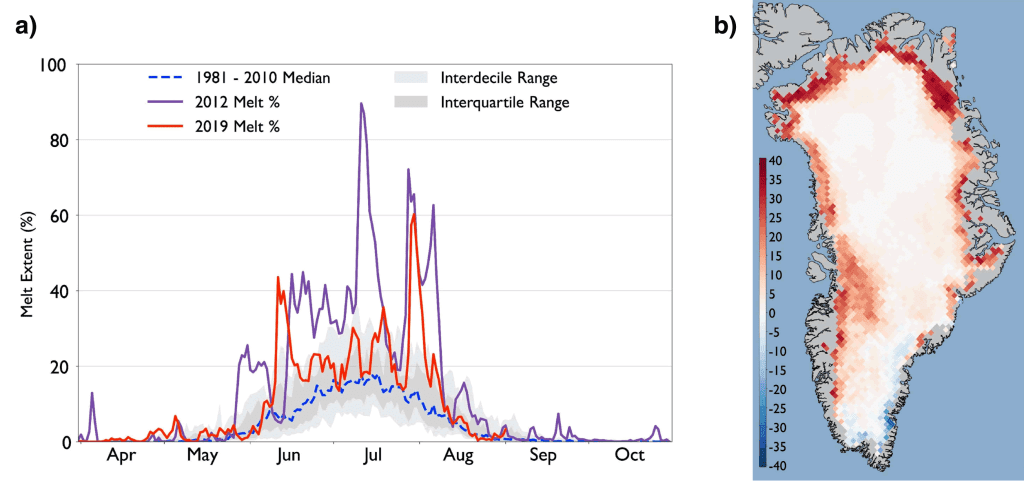
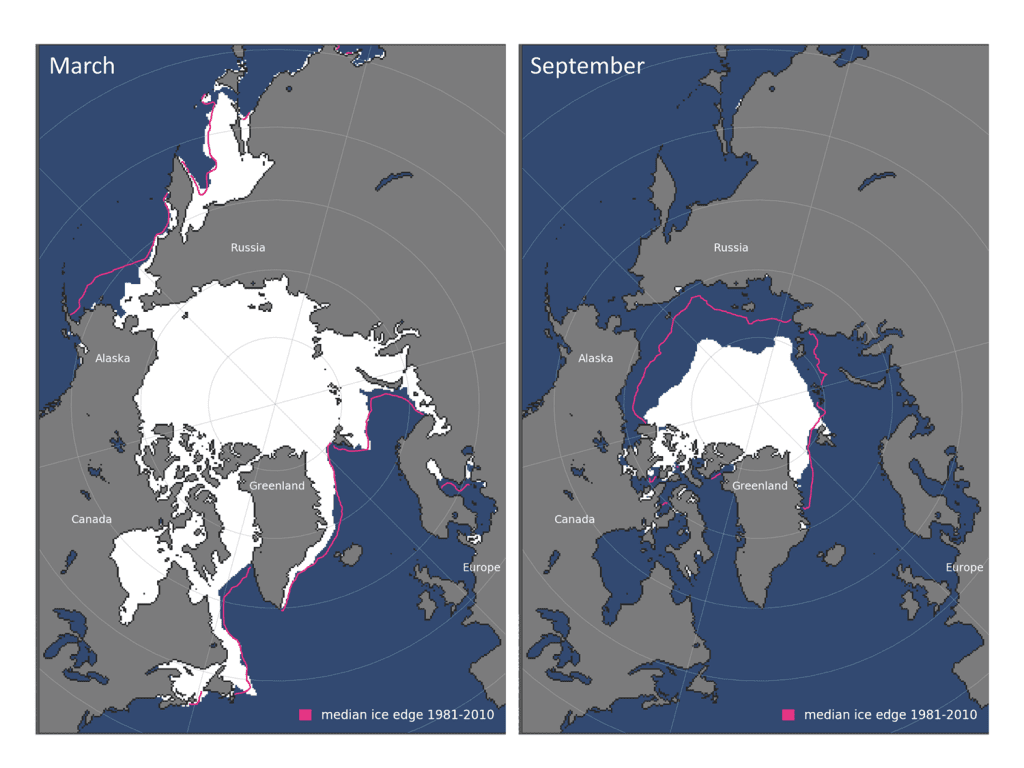
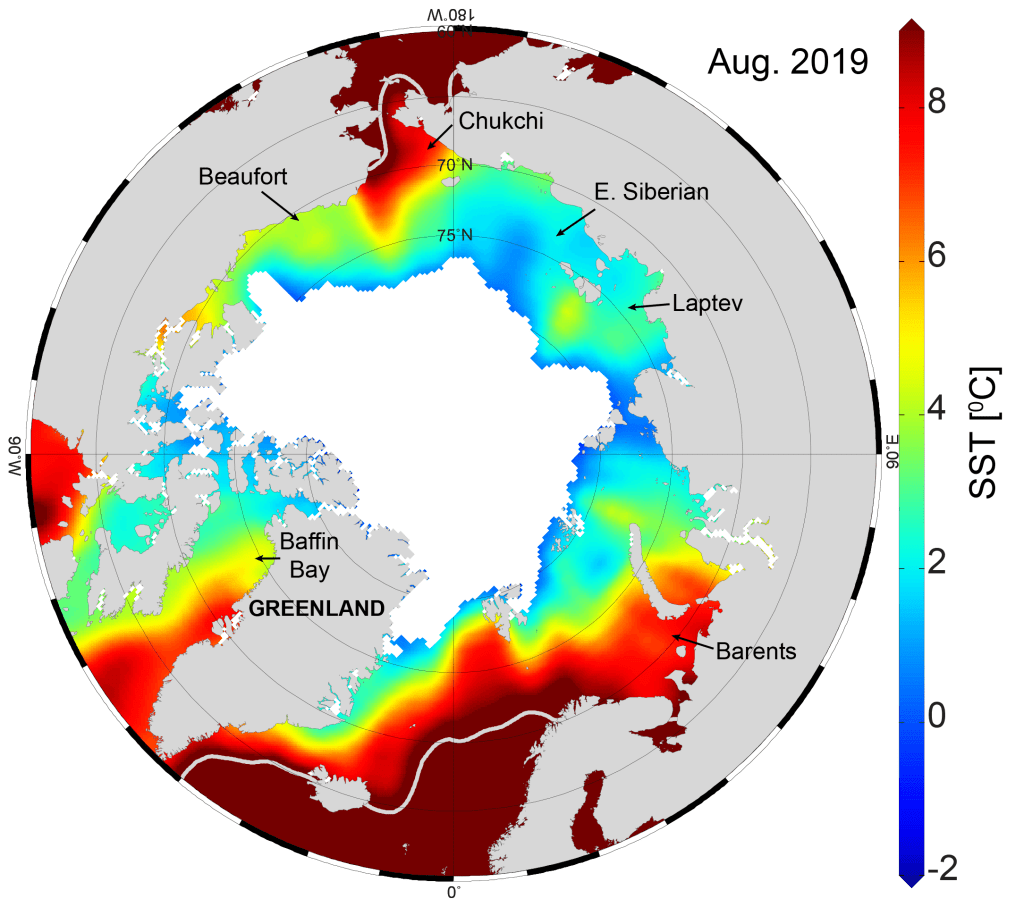
Snow covers the Arctic land surface (land areas north of 60° N) for up to 9 months each year, and influences the surface energy budget, ground thermal regime, and freshwater budget of the Arctic.
Terrestrial Snow Cover Read More »